US Household Income Forecast: 2.5% Rise Predicted for 2025

Experts project a 2.5% increase in US household disposable income for 2025, reflecting a complex interplay of wage growth, employment trends, and persistent inflationary forces.
The latest US Household Income Forecast indicates a promising 2.5% rise in disposable income for 2025, a development that could significantly shape the financial landscape for millions of American families. This projection arrives amidst a period of considerable economic flux, where persistent inflationary pressures continue to challenge household budgets and consumer purchasing power. Understanding the nuances of this forecast is crucial for individuals and policymakers alike as we navigate the evolving economic terrain.
Understanding Disposable Income and Its Importance
Disposable income represents the money households have left to spend or save after taxes and other mandatory deductions. It is a critical economic indicator, reflecting the financial health of consumers and their capacity to fuel economic growth through spending. A projected 2.5% increase signals a potential boost in this vital metric.
What Drives Disposable Income?
Several factors converge to influence disposable income. Wage growth, employment levels, and government transfer payments are primary drivers. When wages increase and more people are employed, the collective disposable income of households generally rises. Conversely, higher taxes or reduced government benefits can diminish this figure.
- Wage Growth: Increases in hourly wages and salaries directly contribute to higher take-home pay.
- Employment Levels: A strong job market means more individuals are earning, boosting overall household income.
- Tax Policies: Changes in federal and state tax rates directly impact the amount of money left after deductions.
- Government Transfers: Social security, unemployment benefits, and other programs provide a safety net and income source.
The significance of a rising disposable income extends beyond individual households. It correlates strongly with consumer confidence and spending, which are major components of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). When consumers feel financially secure, they are more likely to make discretionary purchases, invest, and save, thereby stimulating economic activity. This forecasted increase suggests a potential strengthening of the consumer base, offering a positive outlook for various sectors of the economy.
Analyzing the 2.5% Rise: What Factors Are at Play?
The projection of a 2.5% rise in US household disposable income for 2025 is not a standalone figure but a result of intersecting economic forces. Experts consider a blend of labor market trends, inflation dynamics, and policy decisions when formulating such forecasts. Understanding these underlying factors provides a clearer picture of the economic narrative.
Labor Market Dynamics and Wage Growth
A resilient labor market has been a consistent theme in recent economic reports. Despite some fluctuations, unemployment rates have remained relatively low, and job creation continues. This tight labor market often translates into upward pressure on wages as employers compete for talent. Continued wage increases are a significant contributor to the projected rise in disposable income. However, the pace of wage growth must outstrip inflation for households to experience a real increase in purchasing power.
The Role of Inflationary Pressures
Inflation remains a critical variable in the economic equation. While the 2.5% increase in nominal disposable income is positive, its real value is eroded by inflation. If inflation rates remain elevated, the actual purchasing power gained by households might be less than the nominal increase suggests. Economists are closely watching core inflation metrics, which exclude volatile food and energy prices, to gauge underlying price trends. The battle against inflation by the Federal Reserve through interest rate adjustments also plays a crucial role in shaping the economic environment that impacts household finances.
Government Policies and Economic Stimulus
Government fiscal policies, including potential tax adjustments or targeted spending programs, can also influence disposable income. While direct stimulus payments seen during the pandemic are less likely, other policy measures aimed at supporting specific sectors or demographics could indirectly boost household finances. Furthermore, the broader economic policy framework, including trade agreements and regulatory changes, contributes to the overall stability and growth potential that underpins income projections.
In essence, the 2.5% forecast is a complex mosaic of robust employment, ongoing wage negotiations, and the ever-present challenge of managing inflation. The interplay of these elements will ultimately determine the lived experience of American households in 2025.
Inflationary Pressures: A Closer Look at the Impact on Households
While a 2.5% rise in disposable income sounds encouraging, the concurrent presence of inflationary pressures presents a nuanced challenge for US households. The real impact on families is determined by how much their income growth outpaces, or falls behind, the rising cost of living. This section delves deeper into how inflation specifically affects household budgets and purchasing power.
Erosion of Purchasing Power
Inflation, simply put, reduces the purchasing power of money. A dollar today buys less than it did yesterday. For households, this means that even with a nominal increase in disposable income, their ability to afford goods and services might not improve significantly if prices are rising at a similar or faster rate. Essential expenses, such as groceries, housing, and energy, are often the first to feel the brunt of inflation, forcing families to adjust their spending habits.
- Food Costs: Rising prices at the supermarket directly impact weekly budgets and food security.
- Housing Expenses: Rent increases and higher mortgage rates can consume a larger portion of disposable income.
- Energy Prices: Fluctuations in gas and utility costs affect transportation and home heating/cooling, impacting discretionary funds.
- Healthcare: Medical expenses continue to be a significant burden, often rising with broader inflation.
The challenge for households is to maintain their standard of living when inflation is high. This often involves making difficult choices, such as cutting back on non-essential spending, delaying major purchases, or seeking additional income streams. The psychological impact of inflation can also be profound, leading to reduced consumer confidence and increased financial anxiety.
Strategies for Mitigating Inflation’s Effects
Households are not entirely powerless against inflation. Many adopt strategies to protect their financial well-being. This includes budgeting more rigorously, seeking out better deals, and investing in assets that historically perform well during inflationary periods. Some may also explore opportunities for income growth, such as negotiating raises or pursuing side hustles, to ensure their earnings keep pace with rising costs. Financial literacy and proactive planning become even more crucial in an inflationary environment.
Consumer Spending and Economic Growth: The Interplay
The relationship between rising disposable income, consumer spending, and overall economic growth is a fundamental principle of macroeconomics. A 2.5% uptick in US household disposable income for 2025 could act as a significant catalyst, but its effectiveness hinges on how consumers respond to both this income boost and the prevailing inflationary climate. This intricate interplay shapes the trajectory of the national economy.
The Consumer as an Economic Engine
Consumer spending is the largest component of the US economy, typically accounting for about two-thirds of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). When households have more disposable income, they generally have a greater capacity and propensity to spend. This spending drives demand for goods and services, which in turn encourages businesses to increase production, hire more workers, and invest in expansion. It creates a virtuous cycle of economic activity.
Impact on Various Sectors
A rise in disposable income can have a ripple effect across numerous economic sectors. Discretionary spending, in particular, tends to benefit. Sectors like retail, hospitality, entertainment, and travel often see increased activity as consumers feel more secure in their finances. Even essential sectors can experience growth as consumers opt for higher-quality goods or services. However, the allocation of this increased income will be influenced by how much of it is absorbed by inflation.
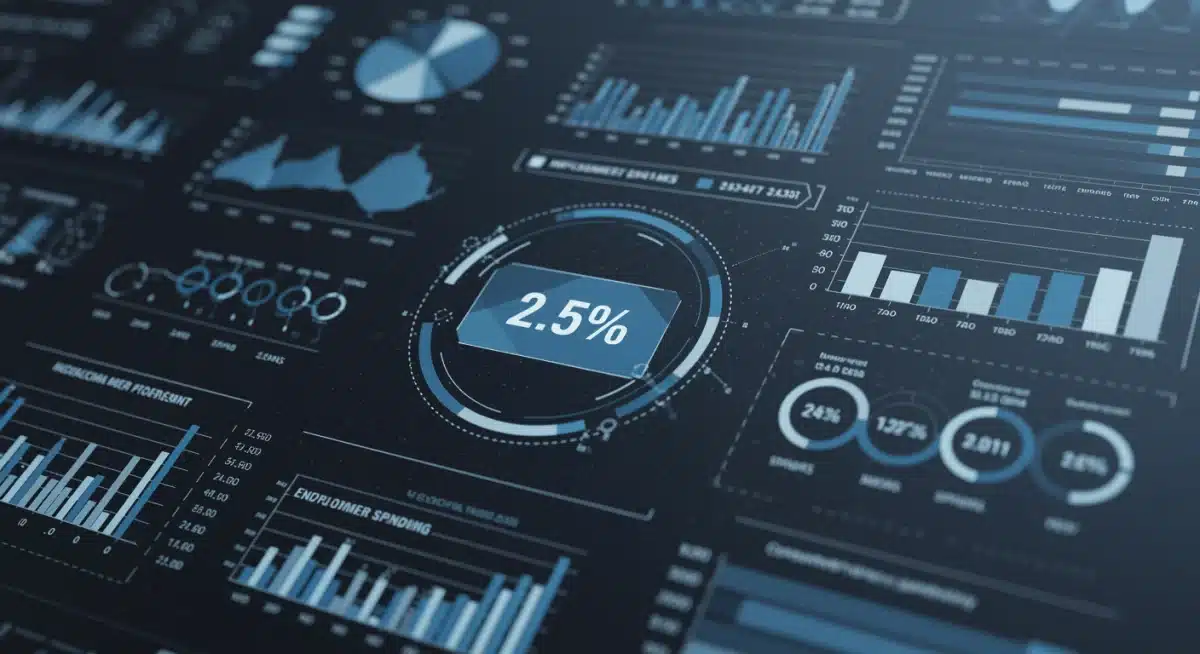

Savings vs. Spending: The Household Dilemma
While increased disposable income often leads to more spending, households also consider saving and debt reduction. In a climate of high inflation, some consumers may choose to save more as a hedge against future price increases or to build a stronger financial buffer. Others might prioritize paying down high-interest debt, which also indirectly strengthens their financial position. The balance between spending and saving will dictate the immediate impact on economic growth. A healthy balance is generally seen as beneficial, ensuring both present demand and future financial stability.
Ultimately, the 2.5% rise in disposable income offers a potential tailwind for the US economy, but its full impact will be modulated by consumer confidence, inflationary pressures, and individual household financial decisions. Policymakers and businesses will be keenly observing these trends to make informed strategic choices.
Regional Disparities and Income Growth
While the forecast of a 2.5% rise in US household disposable income provides a national average, it is crucial to recognize that economic trends rarely manifest uniformly across all regions. The United States is a vast and diverse country, with varying economic structures, cost of living, and labor market dynamics. These regional disparities mean that the impact of income growth and inflationary pressures will be felt differently by households depending on where they reside.
Uneven Wage Growth Across States
Wage growth, a primary driver of disposable income, can vary significantly from one state or metropolitan area to another. Regions with booming industries, such as technology hubs or areas experiencing significant population growth, might see faster wage increases. Conversely, areas with slower economic activity or reliance on industries facing headwinds could experience more modest income gains. This creates a patchwork of economic experiences across the nation.
- High-Growth Areas: States with strong tech, finance, or energy sectors often lead in wage increases.
- Rural vs. Urban: Urban centers typically have higher wages, but also a higher cost of living.
- Industry-Specific Trends: The health of dominant local industries directly impacts regional income levels.
- Labor Market Tightness: Regions with fewer available workers often see employers offering higher wages to attract talent.
The cost of living also plays a pivotal role in how a 2.5% income increase is perceived. A 2.5% rise in disposable income in a state with a low cost of living might translate into a substantial improvement in purchasing power. However, in a high-cost-of-living area, the same percentage increase might barely keep pace with rising expenses, particularly housing and essential services.
Policy Implications for Regional Development
Understanding these regional disparities is vital for effective policymaking. National economic policies, while aiming for broad impact, may need to be complemented by targeted regional initiatives to address specific challenges. For example, infrastructure investments in underserved areas or educational programs tailored to local industry needs can help foster more equitable income growth. Businesses also consider these regional variations when making decisions about expansion, hiring, and compensation, further shaping local economic landscapes.
Preparing for 2025: Strategies for Households and Businesses
With a 2.5% rise in US household disposable income projected for 2025, both households and businesses have an opportunity to strategically plan for the evolving economic environment. While the forecast offers a positive outlook, the persistence of inflationary pressures necessitates careful consideration and adaptive strategies to maximize benefits and mitigate risks.
For Households: Financial Prudence and Planning
For individual households, the projected increase in disposable income presents a chance to strengthen their financial position. This might involve a multi-pronged approach focusing on budgeting, saving, and smart spending.
- Re-evaluate Budgets: Update household budgets to reflect potential income increases and ongoing inflationary costs.
- Prioritize Savings: Allocate a portion of increased disposable income to emergency funds or long-term savings goals.
- Debt Management: Consider using additional income to pay down high-interest debt, reducing financial burden.
- Smart Investing: Explore investment opportunities, potentially in assets that historically perform well during inflation.
- Skill Development: Invest in education or training to enhance earning potential, further boosting future income.
Engaging a financial advisor can also provide personalized guidance, helping families navigate the complexities of managing increased income amidst inflation. The goal is not just to have more money, but to ensure that money works harder for their financial well-being.
For Businesses: Adapting to Consumer Trends
Businesses, particularly those in consumer-facing sectors, must also adapt their strategies. Increased disposable income can translate into higher demand, but inflationary pressures mean consumers will remain price-sensitive and value-conscious. Businesses need to focus on delivering value, optimizing pricing, and understanding evolving consumer preferences.
This involves careful inventory management, efficient supply chain operations to control costs, and innovative marketing strategies to capture consumer attention. Companies that can offer competitive pricing, high-quality products or services, and excellent customer experiences are likely to thrive in this environment. Furthermore, businesses should monitor regional economic trends to tailor their offerings and strategies to specific markets where income growth might be more pronounced or where inflationary impacts differ.
Both households and businesses stand to benefit from proactive planning and a deep understanding of the economic forces at play in 2025. Adaptability and informed decision-making will be key to success.
The Long-Term Outlook: Beyond 2025
While the focus is currently on the US Household Income Forecast for 2025, it is equally important to consider the longer-term economic outlook. Economic trends are rarely static, and the factors influencing disposable income and inflation will continue to evolve. Understanding these potential future shifts allows for more robust planning and adaptation for both individuals and the broader economy.
Demographic Shifts and Labor Force Evolution
Looking beyond 2025, demographic shifts will play an increasingly significant role. An aging population, changes in birth rates, and immigration patterns will all influence the size and composition of the labor force. These shifts can impact wage growth, employment levels, and ultimately, disposable income. Automation and technological advancements will also continue to reshape job markets, creating new opportunities while potentially displacing others, requiring a focus on continuous skill development.
Global Economic Influences
The US economy does not operate in isolation. Global economic conditions, including international trade relations, geopolitical events, and the economic performance of major trading partners, will continue to exert influence. Supply chain resilience, energy prices, and global demand for US exports are all factors that can impact domestic inflation and income growth. A stable and predictable global environment generally fosters more consistent economic growth at home.
Climate Change and Resource Scarcity
In the longer term, the economic impacts of climate change and increasing resource scarcity are becoming more pronounced. These factors can affect agricultural output, energy costs, and infrastructure, potentially leading to new forms of inflationary pressure or requiring significant investment that could impact disposable income. The transition to greener economies also presents both challenges and opportunities for job creation and economic restructuring.
The long-term outlook suggests a dynamic economic landscape where adaptability and foresight will be paramount. While the 2.5% projected rise in disposable income for 2025 is a positive indicator, sustained prosperity will depend on how effectively the nation addresses these multifaceted challenges and opportunities beyond the immediate horizon.
| Key Economic Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 2025 Income Forecast | Experts predict a 2.5% rise in US household disposable income. |
| Inflationary Pressures | Ongoing inflation may temper the real purchasing power of income gains. |
| Consumer Spending | A key driver for economic growth, influenced by disposable income and confidence. |
| Regional Disparities | Income growth and inflation impact vary significantly across different US regions. |
Frequently Asked Questions About the 2025 Economic Outlook
Disposable income is the money you have left after taxes and mandatory deductions. It’s what’s available for spending on goods and services, saving, or investing. A higher disposable income generally means more financial flexibility for your family.
A 2.5% rise in nominal income is positive, but its real impact on daily expenses depends on inflation. If inflation is lower than 2.5%, your purchasing power increases. If inflation is higher, your real purchasing power might still decrease, even with more income.
Inflation is crucial because it determines the real value of any income gain. While your nominal income might increase by 2.5%, persistent high inflation can erode that gain, meaning your money buys less. Experts analyze this balance closely.
Yes, economic forecasts are national averages. Income growth and inflationary impacts can vary significantly by region due to local job markets, industries, and cost of living. Some areas may experience faster growth, while others might see more modest changes.
Households can prepare by reviewing their budgets, prioritizing savings and debt reduction, and exploring smart investment strategies. Investing in skill development can also enhance future earning potential. Proactive financial planning is key to navigating economic shifts.
Conclusion
The projected 2.5% rise in US household disposable income for 2025 offers a hopeful signal for American families, indicating a potential strengthening of their financial capacity. This forecast, however, is set against a backdrop of ongoing inflationary pressures, which necessitate a nuanced understanding of its real-world impact. While increased income can fuel consumer spending and economic growth, the erosion of purchasing power due to rising costs remains a critical concern. Both households and businesses are encouraged to adopt strategic planning and adaptive measures—from diligent budgeting and saving to responsive business models—to effectively navigate the evolving economic landscape. The long-term outlook underscores the importance of continuous adaptation to demographic shifts, global influences, and environmental considerations, ensuring sustained economic well-being beyond the immediate horizon.